Introduction
An air conditioning system is a mechanical system that is utilised to regulate indoor temperature and humidity levels to create a comfortable indoor environment.
The air conditioning unit, in cooling mode, removes heat from the occupied space and in heating mode, supplies heat to the occupied space.
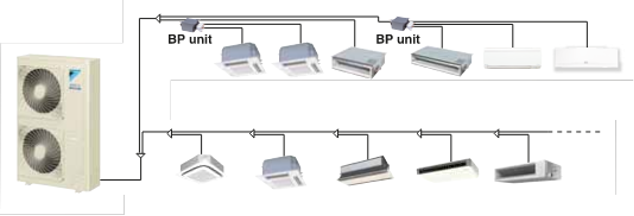
The most common type of air conditioning system used in small to medium sized buildings are of the vapour-compression refrigeration type where the medium of heat transfer is refrigerant. The most common type of refrigerant air conditioning system is the split system.
A split-type air conditioning system comprises of two main sections connected via refrigerant pipework and electrical wiring. There is the outdoor component and the indoor component.
The main components of the outdoor unit comprise of the refrigerant compressor, the heat exchange coil and the expansion valve. The main components of the indoor unit are the indoor fan and the indoor coil.
The two types of split system comprise of the following;
- Single split – an outdoor unit connected to an indoor unit or
- Multi-split / Variable refrigerant flow – an outdoor unit connected to multiple indoor units

Source: Daikin
Common Types of Indoor Air Conditioning Unit:
The most common types of indoor units utilised in Australia are as follows;
In-ceiling ducted indoor air conditioning unit:
 |
This indoor unit is generally installed in the ceiling cavity. It uses ductwork to reticulate conditioned air and grilles / diffusers to introduce this air into the space |
Wall mounted indoor air conditioning unit:

| This indoor unit is mounted on the wall at high level. |
Ceiling mounted cassette indoor air conditioning unit:
 |
The body of the indoor unit is mounted within the ceiling cavity and the fascia panel is exposed.
|
Bulkhead concealed indoor air conditioning unit:
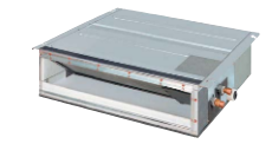 |
The indoor unit is generally installed within a bulkhead with a vertical grille mounted on the surface of bulkhead in front of the unit |
Comparison Between Common Indoor Unit Types
Refer to table below
| Wall mounted unit | Ceiling mounted cassette unit | Bulkhead concealed unit | In-ceiling ducted unit | |
| Aesthetics | Less visually appealing as the unit protrudes from the wall | Fascia of the unit is visible and flushed with with the ceiling. | Unit is within the ceiling and is not exposed. Only grilles / diffusers are visible | Unit is within the ceiling and is not exposed. Only grilles / diffusers are visible |
| Location of unit with respect to the conditioned space | Unit needs to be located in the conditioned space | Unit needs to be located in the conditioned space | Unit is usually located within the ceiling cavity of the conditioned space behind grilles
|
Unit can be located remotely with ductwork reticulating to the conditioned space. |
| Area that can be conditioned by one unit | One room / enclosure. For large enclosures, more than one unit will be required | Usually used for one room / enclosure. Potential for an adjacent space to be provided with minimal conditioned air by a small duct
|
One room / enclosure. For large enclosures, more than one unit will be required
|
Larger areas and is dependent on the capacity of the unit due to the ability to have more grilles / diffusers. |
| Accessibility for maintenance and repairs | Easiest to maintain. Filter change is from the unit that sits lower than a ceiling cassette unit.
|
Easier to maintain than bulkhead concealed and ducted unit. Filter change is via the fascia of the unit, below the ceiling | Hardest to maintain. Unit is usually installed above wardrobes / low height bulkheads with minimal clearance. | Easier to maintain than bulkhead concealed unit due to available higher ceiling space. |
| Indoor Air Quality – cleanliness from dust | Low filtration efficiency as the filters used are low grade and designed to mainly keep the indoor unit coil’s clean | Higher filtration efficiency as compared to wall mounted and bulkhead concealed units but lower than the ducted unit. | Low filtration efficiency as the filters used are low grade and designed to mainly keep the indoor unit coil’s clean | Highest filtration efficiency as higher-grade filters are usually used. |
| Provision of outside air via the unit | No outside air can be provided through the unit.
Outside air supplied directly into space and hence, minimal mixing of unconditioned outside air and return air |
Minimal outside air provision through the unit.
Additional outside air will need to be supplied directly to space.
|
Minimal outside air provision through the unit
Outside air supplied through the bulkhead unit will be higher than the cassette but lesser than the ducted unit |
Highest outside air compared to the other 3 types of indoor units.
Hence, ducted units are generally used where higher amount of outside air required for compliance |
| Noise generation | Unit is mounted within the conditioned space and as such, there will some background noise generated
|
The panel of the unit is mounted within the conditioned space and as such, there will some background noise generated
|
Unit is the quietest as it is situated within the bulkhead and behind a grille
|
Unit is installed within the ceiling cavity and while on its own, the unit is loud, there is potential for noise attenuation |
| Ceiling cavity require-ments | Unit is installed on the wall, below the ceiling. Hence, ceiling cavity is not required. | The body of the unit sits within the ceiling cavity with the fascia panel flushed with the ceiling.
Generally, 300 mm internal height clearance is required for the installation of the unit |
The height of the unit is 200mm.
Generally, 300mm internal height clearance is required for the installation of the unit. |
Highest internal height clearance required in the ceiling cavity.
Generally 600mm internal height clearance is required for the installation of the unit and ductwork |
| Cost | Lowest capital cost.
|
Capital cost is higher than a wall mounted unit but less than a bulkhead or a ducted unit | Including vertical grilles and bulkhead construction, the cost is generally higher than a cassette unit | Highest cost as it includes a plenum for return air and ductwork complete with grilles / diffusers for reticulation of conditioned air |
Here at Essjay Consulting Engineers, through our expertise, we contribute to the creation of environments that enhance the quality of life and support the diverse needs of occupants and communities.
Essjay Consulting Engineers offer a complete building services engineering consultancy. We provide efficient and tailored engineering design solutions for residential, commercial, industrial, fit outs, retail, hotel, supermarket, health sector and educational sectors. We are currently working on multiple nationwide. We are here to guide and walk along the entire design process with you.
If you need to know more about Essjay Consulting Engineers or if you need to discuss about a current building services issue you are having, please do not hesitate to contact any of us.
Suju James – mobile no. 0403 528 471, email – [email protected]
Alex Lee – mobile no, 0468 303 328, email – [email protected]
Josiah Zhou – mobile no. 0416 151 506, email – [email protected]




